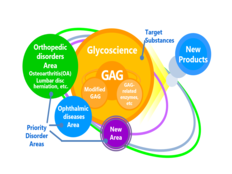
Hyaluronic acid is found throughout our body, and plays various roles.
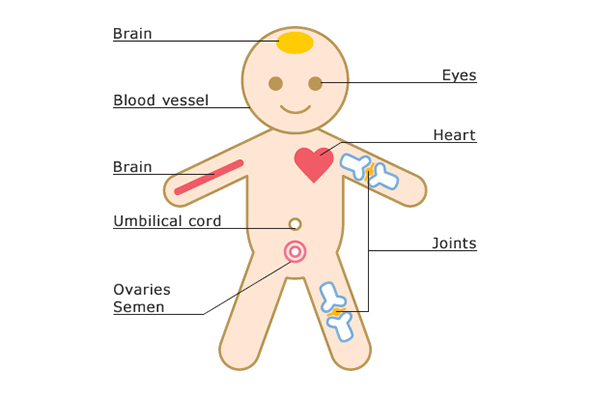
Hyaluronic acid fills the spaces between cells, protecting them by retaining water and serving as a cushion.
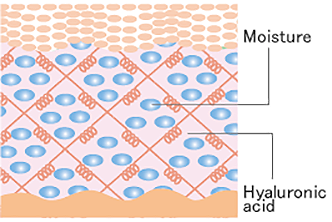
Hyaluronic acid is found abundantly in dermis, helping skin retain its moisture.
Skin with high hyaluronic acid content
The skin remains hydrated and the surface is supple when the skin contains adequate concentrations of hyaluronic acid.
- 拡大
- (Image view)
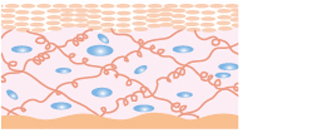
Skin with low hyaluronic acid content
The skin loses its elasticity and the surface becomes dry, because moisture is lost as hyaluronic acid concentrations decrease.
- 拡大
- (Image view)
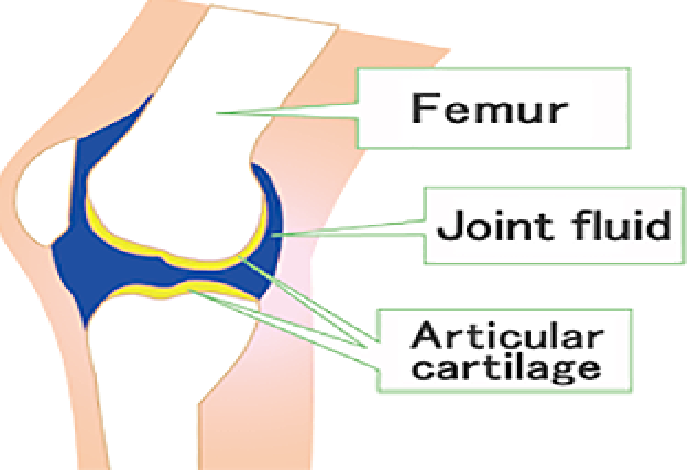
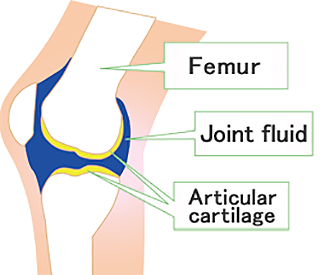
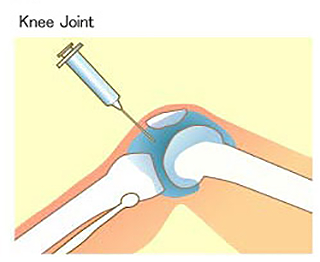
Joint fluid and articular cartilage contain hyaluronic acid at high concentration. It serves as a lubricant (preventing bone-to-bone friction) and as a cushion. This function allows our joints to move smoothly.
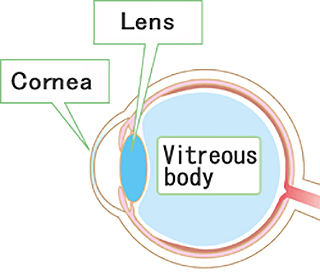
The vitreous body contains high concentrations of hyaluronic acid, where it provides cushioning and plays a role in the maintaining of the shape of the eyeball.
A joint function improving agent with hyaluronic acid as its active pharmaceutical ingredient is a prescription drug. Hyaluronic acid is injected into joints to treat patients suffering from knee osteoarthritis, periarthritis of the shoulder (also known as frozen shoulder syndrome), and knee pain from rheumatoid arthritis. Hyaluronic acid has been reported to have anti-inflammatory and pain relieving effects in such uses.
An ophthalmic viscoelastic device aid made of hyaluronic acid is used during cataract surgery and penetrating keratoplasty. The viscoelasticity of hyaluronic acid helps protect easily damaged cells and is used to secure sufficient intraocular space during surgery.